DEIMOS QuickSlit Data Reduction Tool
Background
The DEIMOS QuickSlit data reduction tool utilizes the DEEP2 DEIMOS spec2d data reduction pipeline to provide a quick reduction of a single slit from a DEIMOS slitmask. The software is intended to be used at the telescope as a "quick-look" tool for inspecting a particular object on a DEIMOS slitmask. The software will perform a full reduction on a single slit from one or more science images acquired with the same slitmask and display the output in the form of both a 2-D sky-subtracted spectrum and a 1-D extracted spectrum.
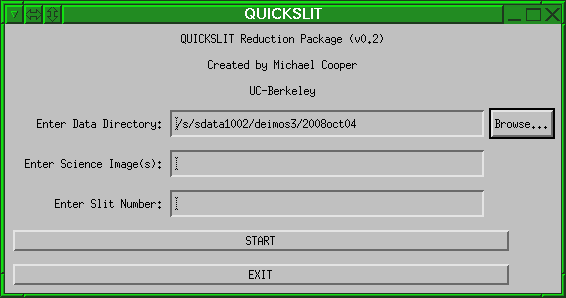
Invocation
The QuickSlit tool is launched called using the following command from any terminal on the data reduction machines (pohue or hamoa) in Remote Ops II.quickslitThis command will launch the main QuickSlit GUI, shown above. The GUI allows the user to specify the following information:
- Directory: the directory in which your data reside. By default, this will be the current DEIMOS data directory. You can alter the directory by editing the text directly or by using the Browse... function to select another directory.
- Images: the (root) names of one or more science frame(s) to employ in the reduction. The user may specify multiple science frames by separating the frame numbers by commas. When multiple frames are passed to QuickSlit, the code will simply co-add the exposures in the multiple science frames. The science frames may be specified by any of the following syntax: "44", "0044", "d0522_0044", or "d522_0044.fits" to specify the science file "d0522_0044.fits". However, if the user has selected a non-standard root filename (e.g. not "d0522_" where 05 specifies the month and 22 specifies the day), then the full image name must be specified (e.g. "d0522_0044" or d0522_0044.fits").
- Slit number: the index number of the slitlet to reduce. You can use the plotmask utility to determine this number if you only know the name of the object you want to analyze.
- The atv window displays the sky-subtracted 2-D image of the slit, sliced into segments and stacked into a rectangular space so that it can be viewed in the image display. The spectrum starts at the top left and continues to the right, then continues on the following line. You can use the atv tool to pan and zoom to view different areas of the spectrum and can adjust the contrast, brightness, and scaling for optimal viewing. Note that in between each line of the sliced-up spectrum is a single line in which the pixel values represent the corresponding wavelength (in Å) for the pixels below that spot. This allows you to determine the wavelength of a given feature.
- The splot window shows the extracted spectrum of the main object in the slit. The target spectrum is in white and the sky spectrum is shown in blue.
Acknowledgement
The QuickSlit tool was designed by Michael Cooper at UC-Berkeley with inspiration and encouragement from Greg Wirth at Keck.See Also
Send questions or comments to:DEIMOS Support