DEIMOS FCS control GUI
This document describes the DEIMOS Flexure Compensation System (FCS) graphical user interface, which can be seen in the following figure:
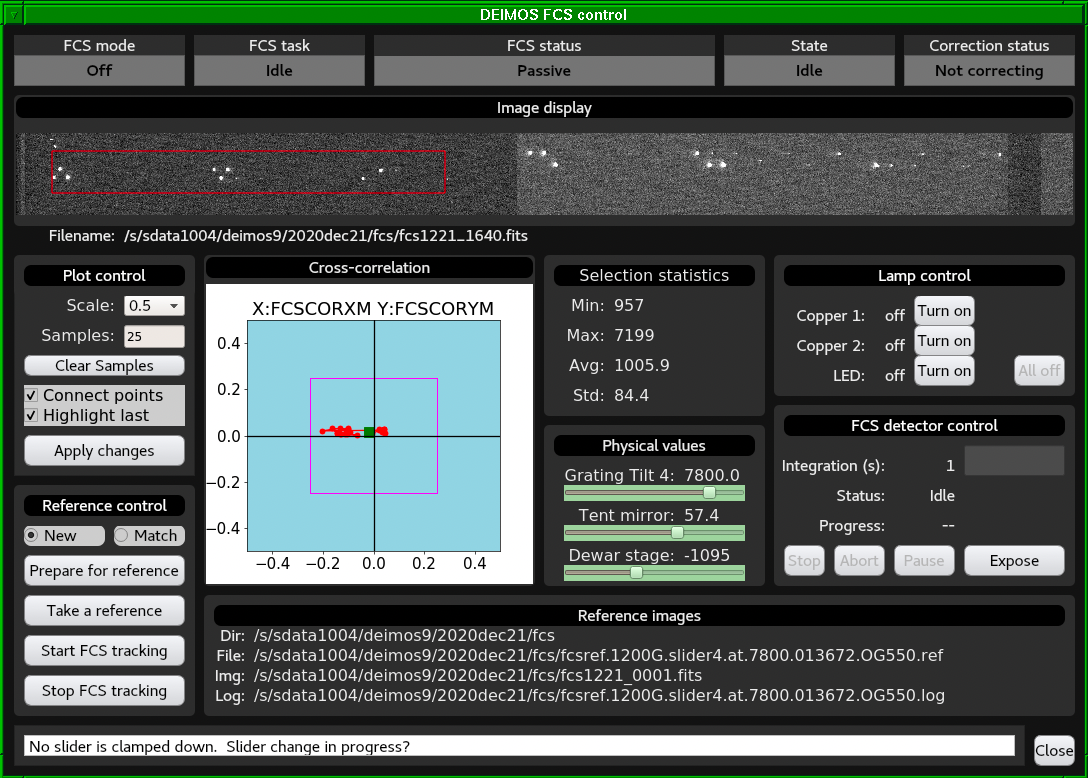
The GUI is divided in different panels or areas:
-
FCS status flags: Show the status of different components
of the FCS tracking loop, which is controller by
the
fcstrackrunning behind the scenes. The most important flag is the FCS status, which is determined as a combination of the FCS mode, task, state and correction status. The FCS status must be Tracking before an science spectral exposure can be started. The The FCS status must be Tracking while an on-sky spectral integration is ongoing. - FCS image display area: Display and analyze FCS images in real time. One can right-click and drag on the image to draw a rectangular region that will be used for statistical analysis.
- Plot control area: Control cross-correlation plot parameters such as zooming (Scale), number of past cross-correlation values to display (Samples) and whether to connect the cross-correlation values or not. Use the Apply changes button to make the changes effective.
- Cross-correlation plot: Monitor the FCS cross-correlation value between the current FCS image and the reference image. The green square symbol shows the current cross-correlation value. The red circular symbols show past cross-correlation values. The purple box shows the region within which the cross-correlation value must be for the FCS status to be Tracking. No on-sky science spectral exposure must be initiated unless the FCS status is Tracking.
- Selection statistics: Show statistics for the rectangular region selected on the FCS image display area. The maximum value in an area containing FCS spots should be larger than 2000 counts to ensure that the cross-correlation signal is high enough for a robust flexure correction.
- FCS stage physical values: Monitor the position of the stages that provide the flexure compensation. The indicator color will change from green to yellow and to red depending on how close a stage is to its travel limit. The grating tilt and tent mirror work together to compensate the flexure in the spectral direction. The dewar stage compensates the flexure in the spatial direction.
-
FCS lamp control: Control the FCS lamps. This is hardly
used, because the lamps are normally handled automatically by
the
fcstrackscript, which manages the flexure compensation system behind the scenes. - FCS detector control: Take FCS individual exposures. This is rarely used, except for resetting the FCS integration time before taking a reference image.
-
Reference control: This area is used to take FCS
reference images. It contains the following buttons:
- New/Match radio buttons: Select whether you want to take a new FCS reference frame or to take a reference frame matching a reference taken on a previous date.
- Prepare for reference: Re-center the FCS control stages and rotate to -30deg, if needed.
- Take a reference: Take an exposure to record a FCS reference image.
- Start FCS tracking: Once you are happy with the FCS reference image for the current optical configuration (combination of grating, central wavelength, filter and focus), you can start the FCS tracking loop.
- Stop FCS tracking: Stop the FCS tracking loop. This is something that you would typically do at the end of an observing night.
- Reference image information: Show the current FCS directory, FCS reference file, FCS reference image and FCS log file for the current optical configuration.
- FCS logging text box: Show relevant logging information for the operation of the flexure compensation system.
- Close button: Use this button to close the FCS GUI.
Send questions or comments to:DEIMOS Support